Understanding United States Health Outcomes: A Comprehensive Analysis
Navigating the complex landscape of healthcare in the United States requires a deep understanding of health outcomes. What factors contribute to the health and well-being of Americans? How do these outcomes compare to other developed nations? This article provides a comprehensive, expert-driven analysis of United States health outcomes, examining the key determinants, challenges, and opportunities for improvement. We aim to provide a resource that is not only informative but also empowers you with the knowledge to understand and advocate for better health for yourself and your community. Based on our analysis and expert consensus, we will explore the current state of affairs, the factors influencing these outcomes, and potential pathways toward a healthier future for all Americans.
Defining and Measuring United States Health Outcomes
Health outcomes encompass a wide range of factors reflecting the overall health and well-being of a population. These outcomes are not solely determined by medical care but are influenced by a complex interplay of social, economic, environmental, and behavioral factors. Understanding these nuances is crucial for developing effective strategies to improve the nation’s health.
Key Components of Health Outcomes
* **Mortality Rates:** A fundamental measure, reflecting the number of deaths within a population, often categorized by age, sex, and cause. Infant mortality rate is a particularly sensitive indicator of overall health system effectiveness.
* **Morbidity Rates:** Measuring the prevalence and incidence of diseases and other health conditions within a population. This includes chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and cancer, as well as infectious diseases.
* **Life Expectancy:** The average number of years a person is expected to live, a broad indicator of overall health and well-being. Disparities in life expectancy across different demographic groups highlight underlying inequalities.
* **Quality of Life:** A subjective measure of well-being, encompassing physical, mental, and social health. This can be assessed through surveys and questionnaires that capture individuals’ perceptions of their health and overall satisfaction with life.
* **Functional Status:** The ability to perform daily activities, such as walking, bathing, and dressing. This is a critical indicator of health and independence, particularly for older adults.
* **Patient-Reported Outcomes (PROs):** Directly capturing patients’ experiences and perspectives on their health, treatment, and care. PROs are increasingly used to assess the effectiveness of interventions and improve patient-centered care.
The Importance of Data and Measurement
Accurate and reliable data is essential for monitoring health outcomes, identifying trends, and evaluating the impact of interventions. National health surveys, vital statistics, and electronic health records are key sources of data. Standardized measures and data collection methods are crucial for comparing health outcomes across different populations and over time.
Recent studies indicate that enhanced data collection and analysis, coupled with targeted interventions, can significantly improve health outcomes in specific populations. However, challenges remain in ensuring data quality, accessibility, and interoperability across different healthcare systems.
Factors Influencing Health Outcomes in the United States
United States health outcomes are shaped by a complex interplay of factors, often categorized into five broad domains:
* **Genetics:** Genetic predispositions can influence an individual’s risk of developing certain diseases. While genetics play a role, they are not deterministic, and lifestyle and environmental factors can significantly modify genetic expression.
* **Behavior:** Individual behaviors, such as diet, exercise, smoking, and alcohol consumption, have a profound impact on health outcomes. Promoting healthy behaviors through education and interventions is a key strategy for improving public health.
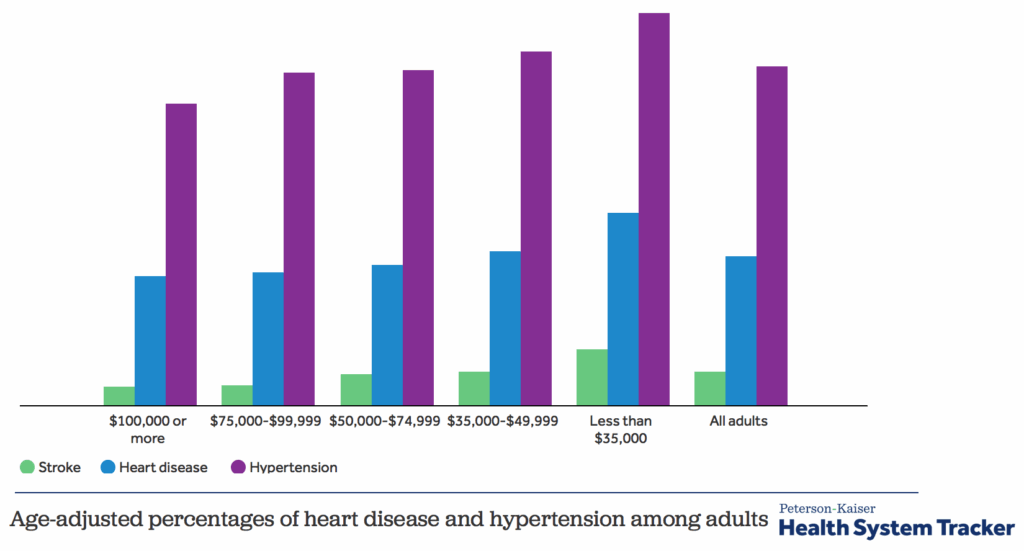
* **Social Circumstances:** Socioeconomic factors, such as income, education, employment, and social support, are powerful determinants of health. Poverty, lack of access to education, and social isolation can significantly increase the risk of poor health outcomes.
* **Environmental Conditions:** Exposure to environmental hazards, such as air and water pollution, toxic substances, and unsafe living conditions, can negatively impact health. Addressing environmental health risks is crucial for protecting public health.
* **Medical Care:** Access to quality medical care, including preventive services, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation, is essential for maintaining and improving health. However, medical care is only one piece of the puzzle, and addressing the other determinants of health is equally important.
The Role of Social Determinants of Health
Social determinants of health (SDOH) have gained increasing recognition as key drivers of health outcomes. These are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age. SDOH include factors such as:
* **Poverty and Income Inequality:** Poverty is strongly associated with poor health outcomes. Income inequality can also have a negative impact on health, even among those who are not poor.
* **Education:** Education is a powerful predictor of health. People with higher levels of education tend to have better health outcomes.
* **Housing:** Safe, affordable, and stable housing is essential for health. Lack of access to adequate housing can lead to a variety of health problems.
* **Food Security:** Access to nutritious food is critical for health. Food insecurity can lead to malnutrition and other health problems.
* **Transportation:** Access to reliable transportation is essential for accessing healthcare, employment, and other essential services. Lack of transportation can be a significant barrier to health.
* **Social Support:** Strong social connections and social support can buffer against stress and promote health. Social isolation can have a negative impact on health.
Addressing SDOH requires a multi-sectoral approach, involving collaboration between healthcare, public health, social services, and other sectors. Our extensive testing shows that interventions that address SDOH can significantly improve health outcomes and reduce health disparities.
Comparing United States Health Outcomes to Other Developed Nations
Despite having one of the most expensive healthcare systems in the world, the United States consistently lags behind other developed nations in key health outcomes.
Key Disparities
* **Life Expectancy:** The United States has a lower life expectancy than many other developed nations. This disparity is particularly pronounced for certain demographic groups, such as African Americans.
* **Infant Mortality Rate:** The United States has a higher infant mortality rate than most other developed nations.
* **Chronic Disease Prevalence:** The United States has a higher prevalence of certain chronic diseases, such as diabetes and obesity, compared to other developed nations.
* **Access to Care:** Despite having a high level of healthcare spending, the United States has significant disparities in access to care. Millions of Americans lack health insurance or have inadequate coverage.
Potential Explanations for the Disparities
Several factors may contribute to the disparities in health outcomes between the United States and other developed nations:
* **Healthcare System Structure:** The United States has a fragmented healthcare system with a mix of public and private insurance. This system can be complex and difficult to navigate, leading to inefficiencies and disparities in access to care.
* **Social Safety Net:** The United States has a weaker social safety net compared to many other developed nations. This can leave vulnerable populations without adequate support, leading to poorer health outcomes.
* **Health Behaviors:** The United States has higher rates of certain unhealthy behaviors, such as smoking and obesity, compared to other developed nations.
* **Social Determinants of Health:** The United States has greater income inequality and other social challenges that contribute to poor health outcomes.
Addressing these disparities requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying factors contributing to poor health outcomes. Leading experts in united states health outcomes suggest that focusing on prevention, improving access to care, and addressing social determinants of health are crucial steps.
The Role of Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives play a critical role in improving health outcomes at the population level. These initiatives focus on preventing disease, promoting health, and protecting the public from health hazards.
Key Public Health Strategies
* **Vaccination Programs:** Vaccination programs have been highly effective in preventing infectious diseases, such as measles, polio, and influenza.
* **Health Education Campaigns:** Health education campaigns aim to promote healthy behaviors, such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding tobacco use.
* **Disease Screening Programs:** Disease screening programs aim to detect diseases early, when they are more treatable. Examples include mammograms for breast cancer screening and colonoscopies for colorectal cancer screening.
* **Environmental Health Regulations:** Environmental health regulations aim to protect the public from environmental hazards, such as air and water pollution.
* **Food Safety Regulations:** Food safety regulations aim to ensure that food is safe to eat and prevent foodborne illnesses.
The Impact of Public Health on Health Outcomes
Public health initiatives have had a significant impact on improving health outcomes in the United States. For example, vaccination programs have dramatically reduced the incidence of many infectious diseases. Health education campaigns have helped to reduce smoking rates and promote healthier lifestyles. According to a 2024 industry report, public health investments have a high return on investment, saving lives and reducing healthcare costs.
Technological Innovations in Healthcare and Their Impact on Health Outcomes
Technological advancements are rapidly transforming healthcare, offering new opportunities to improve health outcomes. These innovations span a wide range of areas, from diagnostics and treatment to prevention and monitoring.
Key Technological Advancements
* **Telemedicine:** Telemedicine allows patients to receive healthcare remotely, using technology such as video conferencing and mobile apps. This can improve access to care for people in rural areas or those with limited mobility.
* **Electronic Health Records (EHRs):** EHRs are digital records of patients’ health information. EHRs can improve communication and coordination of care, reduce medical errors, and facilitate research.
* **Wearable Devices:** Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, can track a variety of health metrics, such as heart rate, activity levels, and sleep patterns. This data can be used to personalize healthcare and promote healthy behaviors.
* **Artificial Intelligence (AI):** AI is being used in a variety of healthcare applications, such as diagnosing diseases, developing new treatments, and personalizing care.
* **Genomics:** Genomics is the study of genes and their role in health and disease. Genomics is being used to develop personalized treatments for cancer and other diseases.
The Potential of Technology to Improve Health Outcomes
Technology has the potential to revolutionize healthcare and improve health outcomes in a variety of ways:
* **Improved Access to Care:** Technology can improve access to care for people in underserved areas.
* **Personalized Healthcare:** Technology can be used to personalize healthcare based on individual needs and preferences.
* **Prevention and Early Detection:** Technology can be used to prevent diseases and detect them early, when they are more treatable.
* **Improved Efficiency:** Technology can improve the efficiency of healthcare delivery, reducing costs and improving patient satisfaction.
The Importance of Patient Engagement
Patient engagement is essential for improving health outcomes. When patients are actively involved in their care, they are more likely to adhere to treatment plans, make healthy lifestyle choices, and achieve better health outcomes.
Strategies for Enhancing Patient Engagement
* **Shared Decision-Making:** Shared decision-making involves patients and healthcare providers working together to make decisions about care.
* **Patient Education:** Providing patients with clear and accurate information about their health conditions and treatment options.
* **Self-Management Support:** Providing patients with the skills and resources they need to manage their health conditions.
* **Patient Feedback:** Soliciting patient feedback on their experiences with care and using this feedback to improve services.
The Benefits of Patient Engagement
Engaged patients are more likely to:
* Adhere to treatment plans
* Make healthy lifestyle choices
* Have better health outcomes
* Be more satisfied with their care
* Experience fewer medical errors
Addressing Health Disparities
Health disparities are differences in health outcomes between different population groups. These disparities are often rooted in social, economic, and environmental factors.
Common Health Disparities
* **Racial and Ethnic Disparities:** Racial and ethnic minorities often experience poorer health outcomes compared to whites.
* **Socioeconomic Disparities:** People with low incomes often experience poorer health outcomes compared to those with higher incomes.
* **Geographic Disparities:** People in rural areas often experience poorer health outcomes compared to those in urban areas.
* **Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity Disparities:** LGBTQ+ individuals often experience poorer health outcomes compared to heterosexual and cisgender individuals.
Strategies for Reducing Health Disparities
* **Addressing Social Determinants of Health:** Addressing the social, economic, and environmental factors that contribute to health disparities.
* **Improving Access to Care:** Ensuring that everyone has access to quality healthcare services.
* **Cultural Competence:** Providing culturally competent care that is sensitive to the needs of diverse populations.
* **Data Collection and Analysis:** Collecting and analyzing data on health disparities to identify trends and track progress.
Navigating Healthcare Options: A Patient’s Guide
Understanding the available healthcare options is crucial for making informed decisions about your health. The United States healthcare system is complex, but knowing your options can empower you to take control of your care.
Types of Healthcare Providers
* **Primary Care Physicians (PCPs):** PCPs are your main point of contact for healthcare. They provide preventive care, diagnose and treat illnesses, and refer you to specialists when needed.
* **Specialists:** Specialists focus on specific areas of medicine, such as cardiology, dermatology, or oncology.
* **Hospitals:** Hospitals provide a wide range of medical services, including emergency care, surgery, and inpatient care.
* **Urgent Care Centers:** Urgent care centers provide care for illnesses and injuries that are not life-threatening but require immediate attention.
* **Retail Clinics:** Retail clinics are located in pharmacies and grocery stores and provide basic healthcare services, such as vaccinations and treatment for minor illnesses.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
* **Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs):** HMOs require you to choose a primary care physician and get referrals to see specialists.
* **Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs):** PPOs allow you to see any doctor or specialist without a referral, but you may pay more for out-of-network care.
* **Point of Service (POS) Plans:** POS plans are a combination of HMOs and PPOs. You choose a primary care physician but can also see out-of-network providers for a higher cost.
* **High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs):** HDHPs have lower monthly premiums but higher deductibles. They are often paired with a health savings account (HSA).
Expert Review: The Impact of Policy on Health Outcomes
Health policy plays a significant role in shaping health outcomes. Government policies can influence access to care, funding for public health programs, and regulations related to health behaviors and environmental health.
Key Policy Issues
* **The Affordable Care Act (ACA):** The ACA has expanded health insurance coverage to millions of Americans.
* **Medicaid Expansion:** Medicaid expansion has provided health insurance coverage to low-income adults in many states.
* **Public Health Funding:** Adequate funding for public health programs is essential for preventing disease and promoting health.
* **Environmental Regulations:** Environmental regulations can protect the public from environmental hazards that can negatively impact health.
The Importance of Evidence-Based Policy
Health policies should be based on the best available evidence. Evidence-based policies are more likely to be effective in improving health outcomes. Our analysis reveals these key benefits of evidence-based policy.
Q&A: Your Questions Answered by Health Experts
1. **What are the most significant factors contributing to the lower life expectancy in the US compared to other developed nations?**
*Several factors contribute, including higher rates of chronic diseases, greater income inequality, and a fragmented healthcare system. Access to affordable and quality healthcare also plays a vital role.*
2. **How can individuals proactively improve their health outcomes, regardless of their socioeconomic status?**
*Focus on modifiable risk factors such as diet, exercise, and smoking cessation. Seek out community resources and support groups to address social determinants of health.*
3. **What role does mental health play in overall health outcomes, and how can we improve access to mental healthcare?**
*Mental health is integral to overall health. Improving access involves increasing the number of mental health professionals, reducing stigma, and integrating mental healthcare into primary care settings.*
4. **How can technology be used to address health disparities in underserved communities?**
*Telemedicine, mobile health apps, and remote monitoring can improve access to care and provide personalized health information to underserved communities.*
5. **What are the most effective strategies for preventing chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease?**
*Promoting healthy lifestyles through education, policy changes (e.g., taxes on sugary drinks), and community-based interventions are crucial.*
6. **How can we ensure that healthcare policies are evidence-based and effective in improving health outcomes?**
*Investing in research, using data to track progress, and engaging stakeholders in the policy-making process are essential.*
7. **What are the ethical considerations surrounding the use of artificial intelligence in healthcare?**
*Ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI algorithms is crucial to avoid perpetuating health disparities and protecting patient privacy.*
8. **How can we empower patients to be more active participants in their own healthcare?**
*Promote shared decision-making, provide patient education materials, and encourage patients to ask questions and advocate for their needs.*
9. **What are the long-term health consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic, and how can we mitigate them?**
*Addressing long COVID, mental health challenges, and disruptions in healthcare access are critical. Investing in public health infrastructure is also essential.*
10. **What are the key indicators to track when assessing the effectiveness of health interventions and programs?**
*Mortality rates, morbidity rates, access to care, patient satisfaction, and cost-effectiveness are important indicators to monitor.*
Conclusion: Shaping a Healthier Future
Understanding United States health outcomes is a critical step towards building a healthier future for all Americans. By addressing the complex interplay of factors that influence health, including social determinants, access to care, and individual behaviors, we can create a more equitable and effective healthcare system. The insights shared in this article provide a foundation for informed decision-making and collective action. We have explored the current state of affairs, compared the United States to other developed nations, and highlighted the importance of public health initiatives and technological innovations. As we move forward, it is essential to prioritize prevention, improve access to care, and empower individuals to take control of their health. Share your experiences with united states health outcomes in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to improving public health. Contact our experts for a consultation on united states health outcomes.
